Estúdio Horácio Novais, Estação do rossio, Lisboa, sem data Colecções daFundação Calouste Gulbenkian, Lisboa, Portugal (Flickr Commons)
2017-02-13
Astronomy picture of the day - 2017 February 13 - Cloud Swirls around Southern Jupiter from Juno
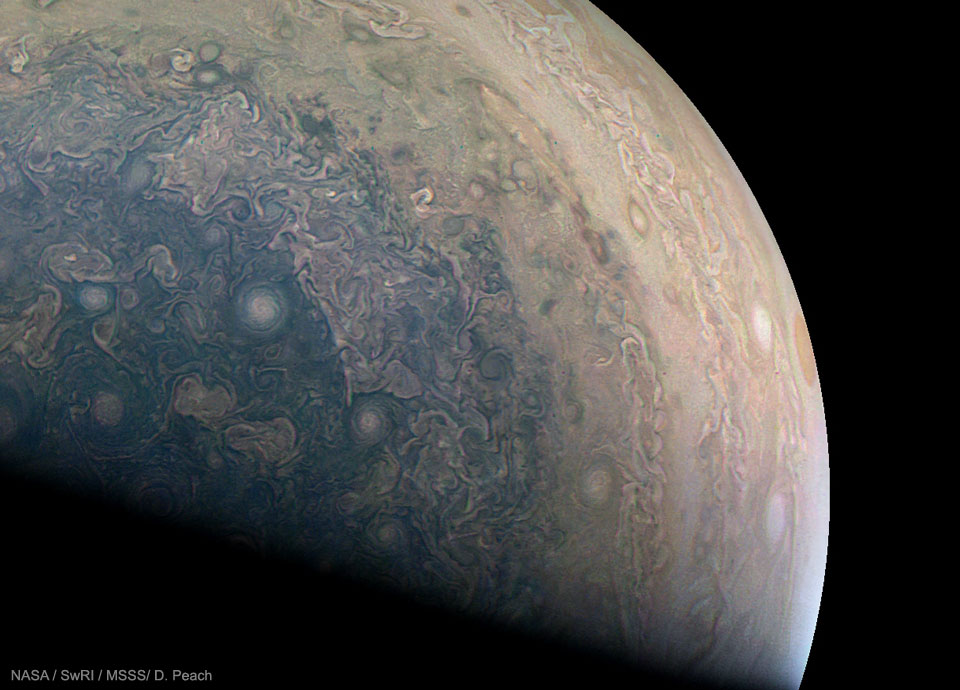

Image Credit: NASA, JPL-Caltech, SwRI, MSSS; Processing: Damian Peach
Explanation: Juno just completed its fourth pass near Jupiter. Launched from Earth in 2011 and arriving at Jupiter just last July, robotic Juno concluded its latest elliptical orbit around our Solar System's largest planet 11 days ago.Pictured here from that pass is a new high-resolution image of the southern hemisphere of Jupiter featuring a mesmerizing tapestry of swirling cloud systems. The terminator between day and night cuts diagonally across the bottom, meaning that the Sun is positioned off the top right. Large Oval BA is visible in orange on the far right. Reasons for the details and colors of Jupiter's cloud swirls are currently unknown. Juno planned six year mission will study Jovian giant in new ways, including trying to determine if beneath its thick clouds, Jupiter has a solid core.
2017-02-12
Astronomy picture of the day - 2017 February 12 - Comet 45P Passes Near the Earth
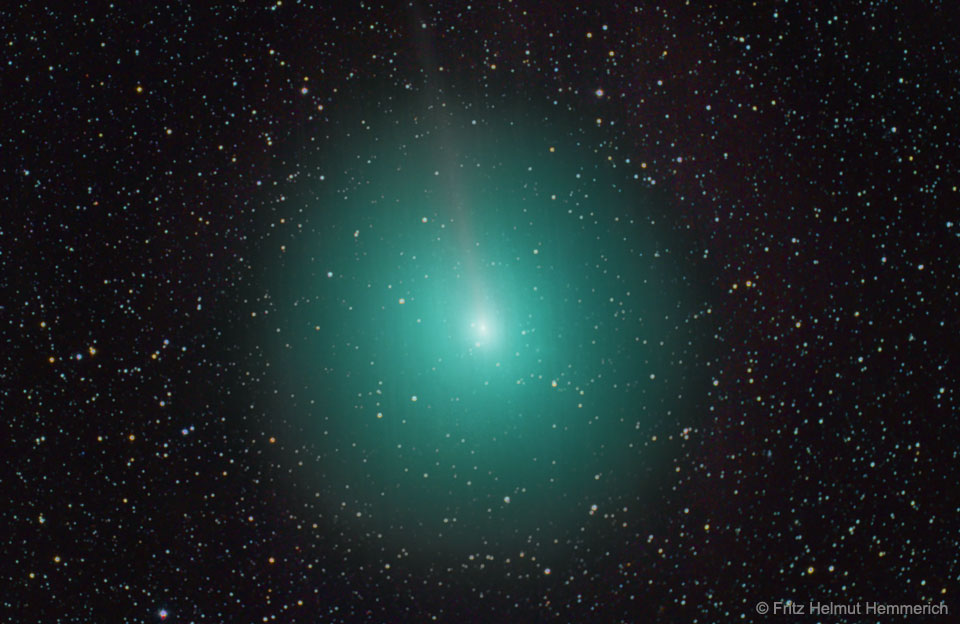

Image Credit & Copyright: Fritz Helmut Hemmerich
Explanation: A large snowball has just passed the Earth. Known as Comet 45P/Honda–Mrkos–Pajdušáková", or 45P for short, the comet came 10 times closer to Earth yesterday than the Earth ever gets to the Sun. During this passage, the comet was photographed sporting a thin ion tail and a faint but expansive green coma. The green color is caused mostly by energized molecules of carbon. Comet 45P became just bright enough to see with the unaided eyewhen it came closest to the Sun in December. Now, however, the comet is fading as it heads back out to near the orbit of Jupiter, where it spends most of its time. The kilometer-sized nucleus of ice and dirt will return to the inner Solar System in 2022.
2017-02-11
Astronomy picture of the day - 2017 February 11 - Solar System Portrait
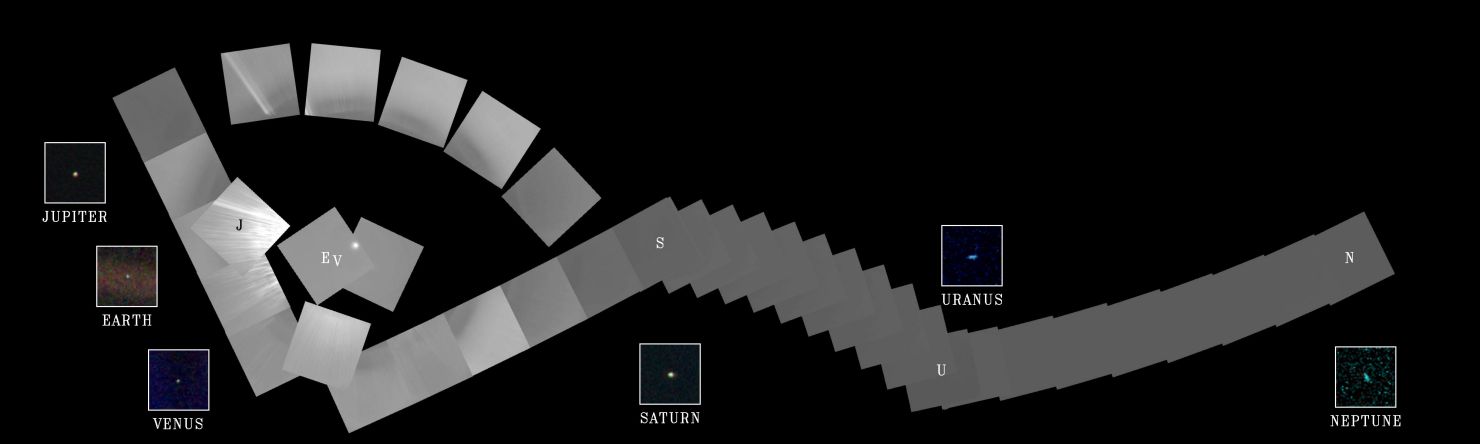
Image Credit: Voyager Project, NASA
Explanation: On Valentine's Day in 1990, cruising four billion miles from the Sun, the Voyager 1 spacecraft looked back one last time to make this first ever Solar System family portrait. The complete portrait is a 60 frame mosaicmade from a vantage point 32 degrees above the ecliptic plane. In it, Voyager's wide angle camera frames sweep through the inner Solar System at the left, linking up with gas giant Neptune, the Solar System's outermost planet, at the far right. Positions for Venus, Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are indicated by letters, while the Sun is the bright spot near the center of the circle of frames. The inset frames for each of the planets are from Voyager's narrow field camera. Unseen in the portrait are Mercury, too close to the Sun to be detected, and Mars, unfortunately hidden by sunlight scattered in the camera's optical system. Closer to the Sun than Neptune at the time, small, faint Pluto's position was not covered.
2017-02-10
Astronomy picture of the day - 2017 February 10 - Melotte 15 in the Heart
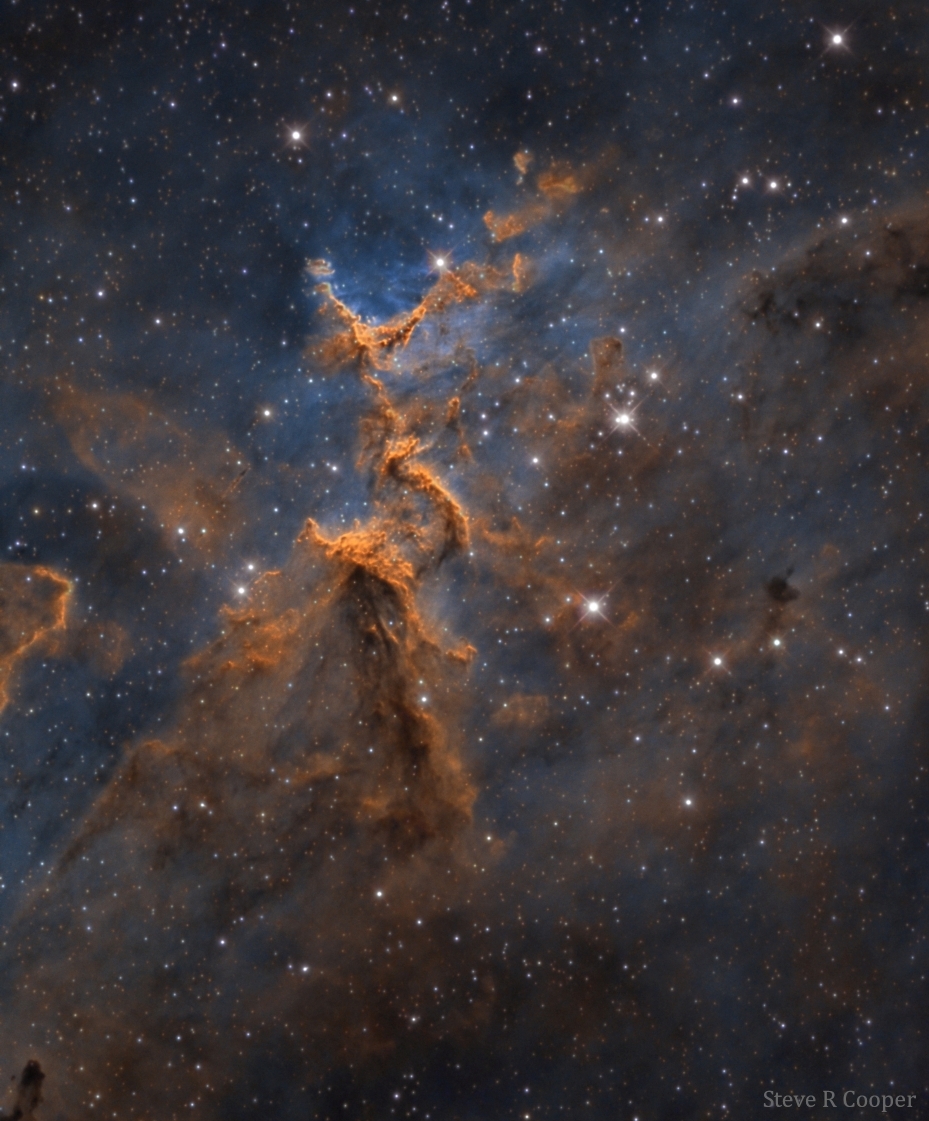

Image Credit & Copyright: Steve Cooper
Explanation: Cosmic clouds form fantastic shapes in the central regions of emission nebula IC 1805. The clouds are sculpted by stellar winds and radiation from massive hot stars in the nebula's newborn star cluster, Melotte 15. About 1.5 million years young, the cluster stars are scattered in this colorful skyscape, along with dark dust clouds in silhouette against glowing atomic gas. A composite of narrowband and broadband telescopic images, the view spans about 15 light-years and includes emission from ionized hydrogen, sulfur, and oxygen atoms mapped to green, red, and blue hues in the popular Hubble Palette. Wider field images reveal that IC 1805's simpler, overall outline suggests its popular name - The Heart Nebula. IC 1805 is located about 7,500 light years away toward the boastful constellation Cassiopeia.
2017-02-09
Astronomy picture of the day - 2017 February 9 - Crescent Enceladus
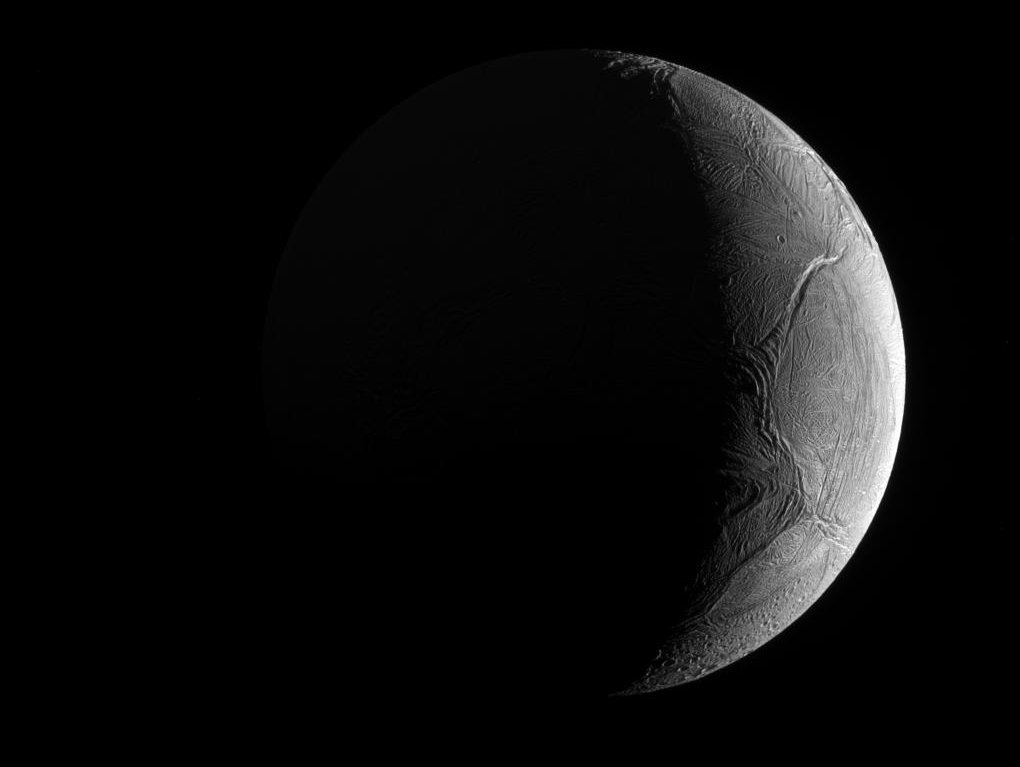

Image Credit: Cassini Imaging Team, SSI, JPL, ESA, NASA
Explanation: Peering from the shadows, the Saturn-facing hemisphere of tantalizing inner moon Enceladus poses in this Cassini spacecraft image. North is up in the dramatic scene captured last November as Cassini's camera was pointed in a nearly sunward direction about 130,000 kilometers from the moon's bright crescent. In fact, the distant world reflects over 90 percent of the sunlight it receives, giving its surface about the same reflectivity as fresh snow. A mere 500 kilometers in diameter, Enceladus is a surprisingly active moon. Data collected during Cassini's flybys and years of images have revealed the presence of remarkable south polar geysers and a possible global ocean of liquid water beneath an icy crust.
2017-02-08
Astronomy picture of the day - 2017 February 8 - The Butterfly Nebula from Hubble
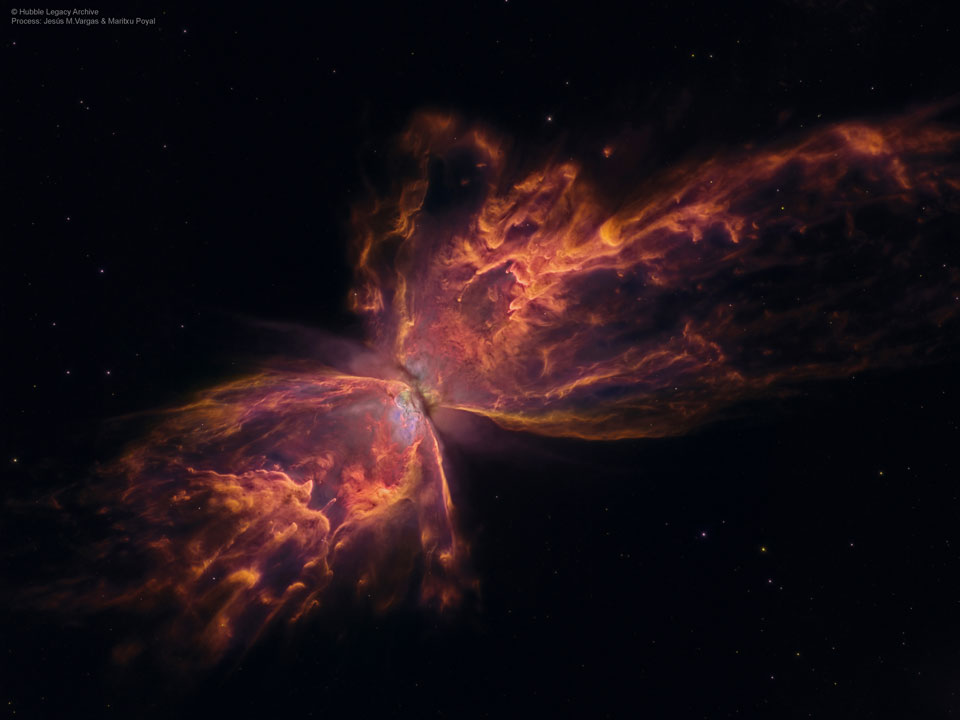

Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble, HLA; Reprocessing & Copyright: Jesús M.Vargas & Maritxu Poyal
Explanation: The bright clusters and nebulae of planet Earth's night sky are often named for flowers or insects. Though its wingspan covers over 3 light-years, NGC 6302 is no exception. With an estimated surface temperature of about 250,000 degrees C, the dying central star of this particular planetary nebula has become exceptionally hot, shining brightly in ultraviolet light but hidden from direct view by a dense torus of dust. This sharp close-up of the dying star's nebula was recorded by the Hubble Space Telescope and is presented here in reprocessed colors. Cutting across a bright cavity of ionized gas, the dust torus surrounding the central star is near the center of this view, almost edge-on to the line-of-sight. Molecular hydrogen has been detected in the hot star's dusty cosmic shroud. NGC 6302 lies about 4,000 light-years away in the arachnologically correct constellation of the Scorpion (Scorpius).
Inscription à :
Commentaires (Atom)

