"In the Army now"
2018-03-09
Astronomy picture of the day - 2018 March 9 - Horsehead: A Wider View
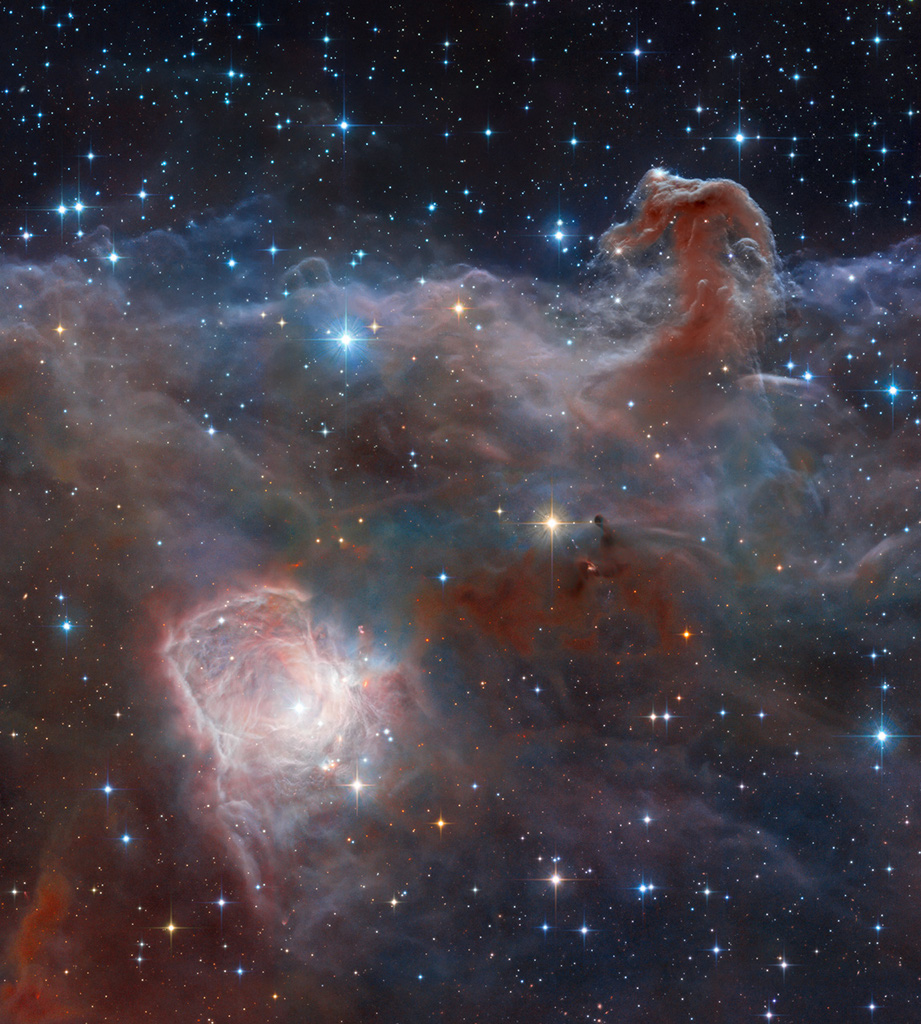

Composition and Processing: Robert Gendler
Image Data: ESO, VISTA, HLA, Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
Explanation: Combined image data from the massive, ground-based VISTA telescope and the Hubble Space Telescope was used to create this wide perspective of the interstellar landscape surrounding the famous Horsehead Nebula. Captured at near-infrared wavelengths, the region's dusty molecular cloud sprawls across the scene that covers an angle about two-thirds the size of the Full Moon on the sky. Left to right the frame spans just over 10 light-years at the Horsehead's estimated distance of 1,600 light-years. Also known as Barnard 33, the still recognizable Horsehead Nebula stands at the upper right, the near-infrared glow of a dusty pillar topped with newborn stars. Below and left, the bright reflection nebula NGC 2023 is itself the illuminated environs of a hot young star. Obscuring clouds below the base of the Horsehead and on the outskirts of NGC 2023 show the tell-tale far red emission of energetic jets, known as Herbig-Haro objects, also associated with newborn stars.
2018-03-08
Astronomy pictures of the day - 2018 March 8 - Cyclones at Jupiter's North Pole
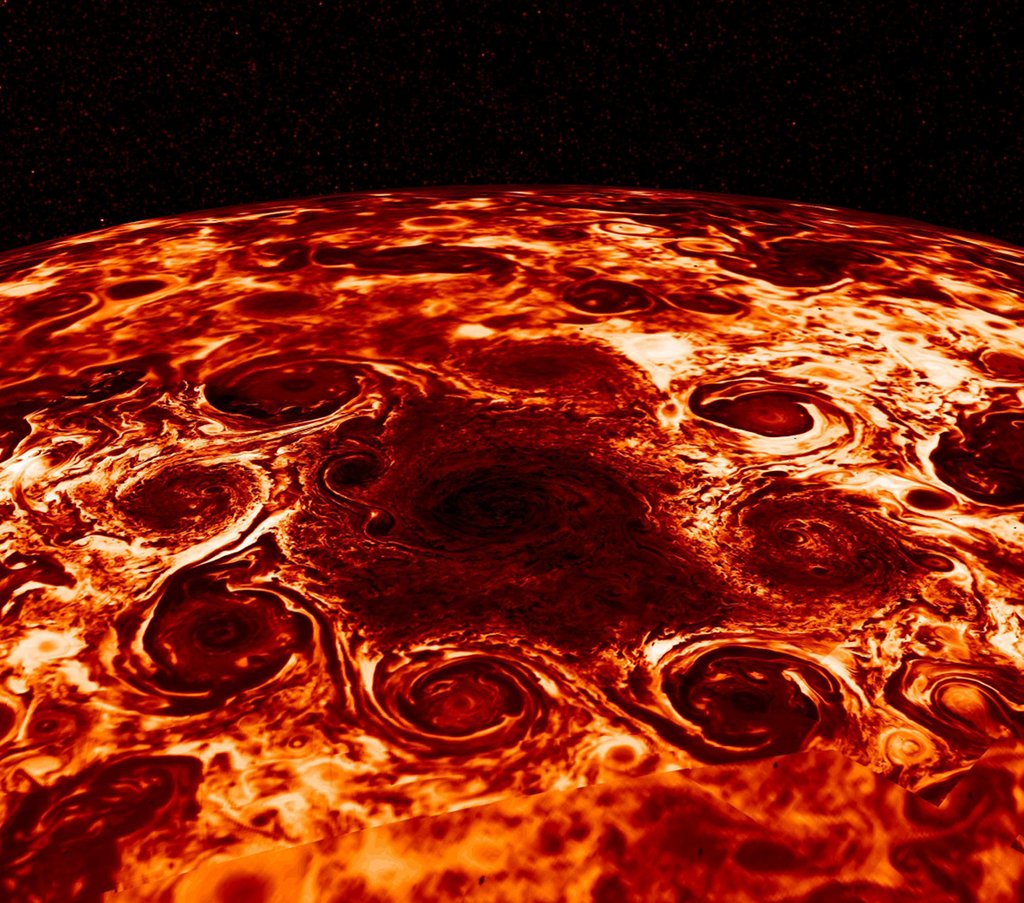
Image Credit: NASA, JPL-Caltech, SwRI, ASI, INAF, JIRAM
Explanation: Juno's Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper data was used to construct this stunning view of cyclones at Jupiter's North Pole. Measuring the thermal emission from Jovian cloud tops, the infrared the observations are not restricted to the hemisphere illuminated by sunlight. They reveal eight cyclonic features that surround a cyclone about 4,000 kilometers in diameter, just offset from the giant planet's geographic North Pole. Similar data show a cyclone at the Jovian South Pole with five circumpolar cyclones. The South Pole cyclones are slightly larger than their northern cousins. Cassini data has shown that gas giant Saturn's north and south poles each have a single cyclonic storm system.
2018-03-07
Astronomy picture of the day - 2018 March 7 - Arcs, Jets, and Shocks near NGC 1999
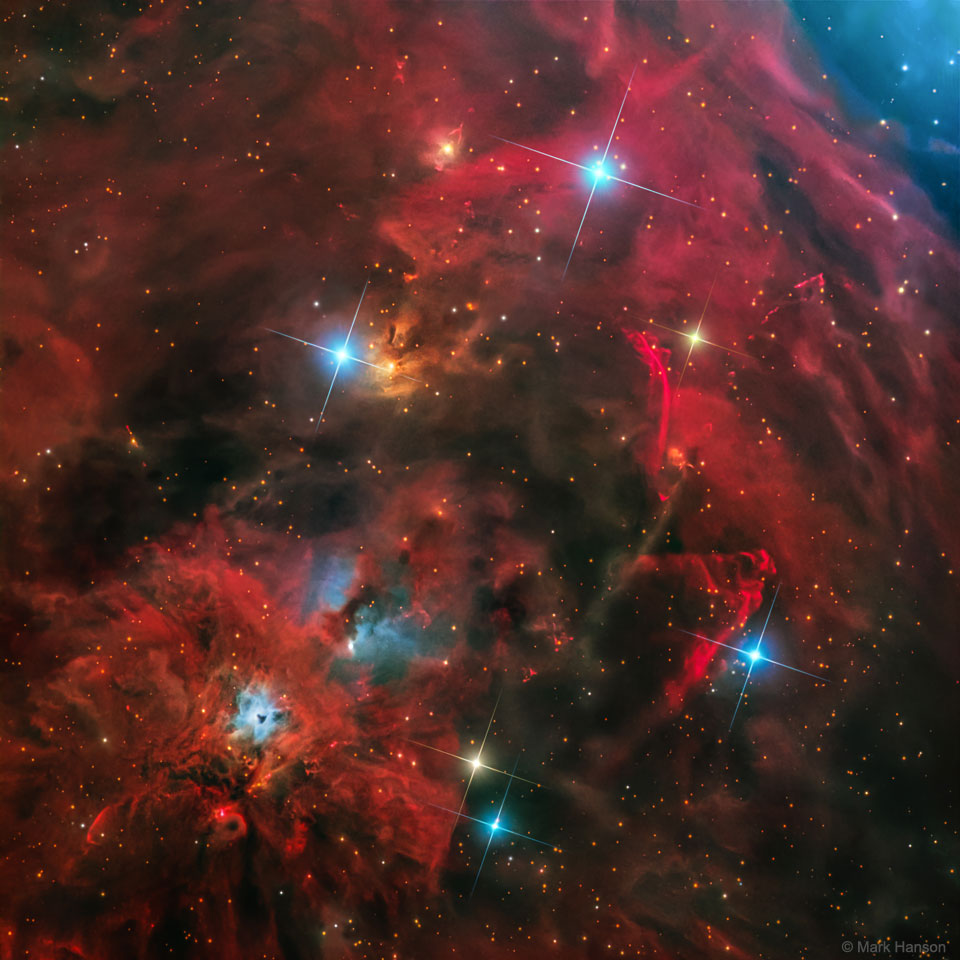

Image Credit & Copyright: Mark Hanson
Explanation: This tantalizing array of nebulas and stars can be found about two degrees south of the famous star-forming Orion Nebula. The region abounds with energetic young stars producing jets and outflows that push through the surrounding material at speeds of hundreds of kilometers per second. The interaction creates luminous shock waves known as Herbig-Haro (HH) objects. For example, the graceful, flowing arc just right of center is cataloged as HH 222, also called the Waterfall Nebula. Seen below the Waterfall, HH 401 has a distinctive cone shape. The bright bluish nebula below and left of center is NGC 1999, a dusty cloud reflecting light from an embedded variable star. The entire cosmic vista spans over 30 light-years, near the edge of the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex some 1,500 light-years distant.
2018-03-06
Astronomy picture of the day - 2018 March 6 - Colorful Airglow Bands Surround Milky Way
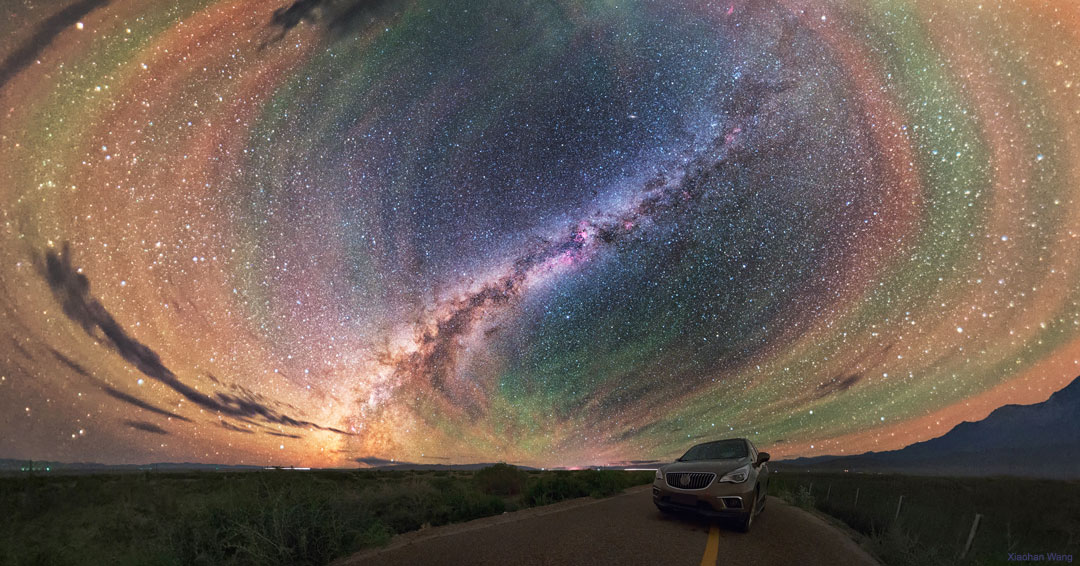

Image Credit & Copyright: Xiaohan Wang
Explanation: Why would the sky glow like a giant repeating rainbow? Airglow. Now air glows all of the time, but it is usually hard to see. A disturbance however -- like an approaching storm -- may cause noticeable rippling in theEarth's atmosphere. These gravity waves are oscillations in air analogous to those created when a rock is thrown in calm water. Red airglow likely originates from OH molecules about 87-kilometers high, excited by ultraviolet light from the Sun, while orange and green airglow is likely caused by sodium and oxygen atoms slightly higher up. While driving near Keluke Lake in Qinghai Provence in China, the photographer originally noticed mainly the impressive central band of the Milky Way Galaxy. Stopping to photograph it, surprisingly, the resulting sensitive camera image showed airglow bands to be quite prominent and span the entire sky. The featured image has been digitally enhanced to make the colors more vibrant.
Inscription à :
Commentaires (Atom)

