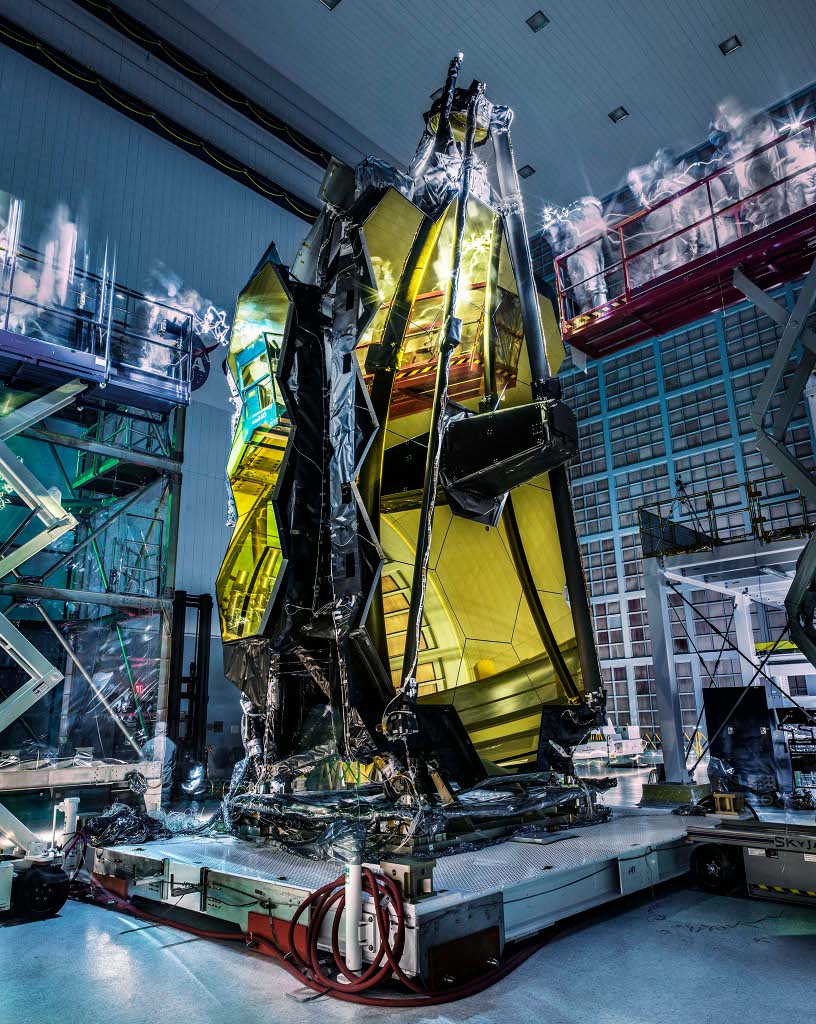
 JWST: Ghosts and Mirrors
JWST: Ghosts and Mirrors
Image Credit: Chris Gunn, NASA
Explanation: Ghosts aren't actually hovering over the James Webb Space Telescope. But the lights are out as it stands with gold tinted mirror segments and support structures folded in Goddard Space Flight Center's Spacecraft Systems Development and Integration Facility clean room. Following vibration and acoustic testing, bright flashlights and ultraviolet lights are played over the stationary telescope looking for contamination, easier to spot in a darkened room. In the dimness the camera's long exposure creates the ghostly apparitions, blurring the moving lights and engineers. A scientific successor to Hubble, the James Webb Space Telescope is optimized for the infrared exploration of the early Universe. Its planned launch is in 2018 from French Guiana on a European Space Agency Ariane 5 rocket.
Estúdio Mário Novais, padrão dos Descobrimentos e espelho de água, lisboa, 1940 Colecções da Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian, Lisboa, Portugal (Flickr Commons)
 Phases of Venus
Phases of Venus
Image Credit & Copyright: Daniel Herron
Explanation: Just as the Moon goes through phases, Venus' visible sunlit hemisphere waxes and wanes. This composite of telescopic images illustrates the steady changes for the inner planet, seen in the west as the evening star, as Venus grows larger but narrows to a thin crescent from December 20, 2016 through March 10. Gliding along its interior orbit between Earth and Sun, Venus grows larger during that period because it is approaching planet Earth. Its crescent narrows, though, as Venus swings closer to our line-of-sight to the Sun. Closest to the Earth-Sun line but passing about 8 degrees north of the Sun on March 25, Venus will reach a (non-judgmental) inferior conjunction. Soon after, Venus will shine clearly above the eastern horizon in predawn skies as planet Earth's morning star.
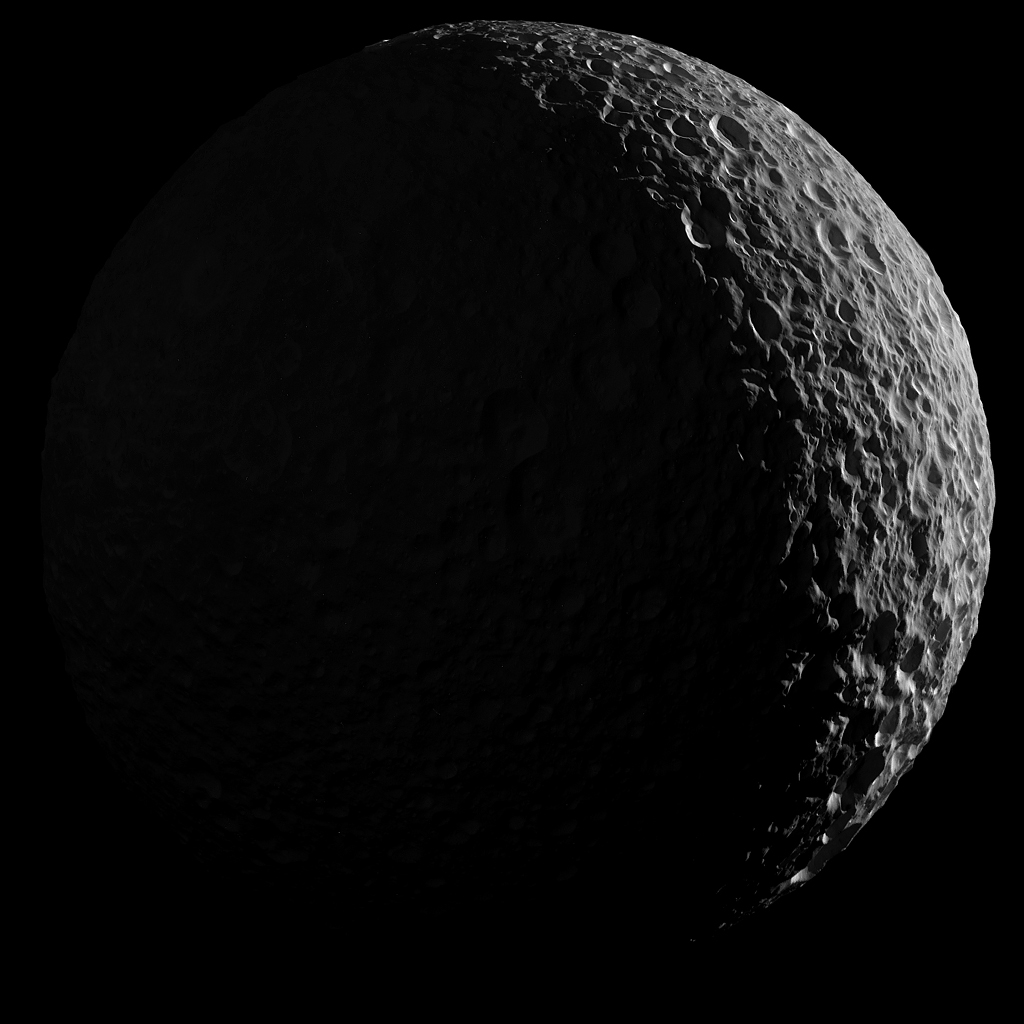 Mimas in Saturnlight
Mimas in Saturnlight
Image Credit: Cassini Imaging Team, SSI, JPL, ESA, NASA
Explanation: Peering from the shadows, the Saturn-facing hemisphere of Mimas lies in near darkness alongside a dramatic sunlit crescent. The mosaic was captured near the Cassini spacecraft's final close approach on January 30, 2017. Cassini's camera was pointed in a nearly sunward direction only 45,000 kilometers from Mimas. The result is one of the highest resolution views of the icy, crater-pocked, 400 kilometer diameter moon. An enhanced version better reveals the Saturn-facing hemisphere of the synchronously rotating moon lit by sunlight reflected from Saturn itself. To see it, slide your cursor over the image (or follow this link). Other Cassini images of Mimas include the small moon's large and ominous Herschel Crater.
 The Cone Nebula from Hubble
The Cone Nebula from Hubble
Image Credit: Hubble Legacy Archive, NASA, ESA - Processing & Licence: Judy Schmidt
Explanation: Stars are forming in the gigantic dust pillar called the Cone Nebula. Cones, pillars, and majestic flowing shapes abound in stellar nurseries where natal clouds of gas and dust are buffeted by energetic winds from newborn stars. The Cone Nebula, a well-known example, lies within the bright galactic star-forming region NGC 2264. The Cone was captured in unprecedented detail in this close-up composite of several observations from the Earth-orbitingHubble Space Telescope. While the Cone Nebula, about 2,500 light-years away in Monoceros, is around 7 light-years long, the region pictured here surrounding the cone's blunted head is a mere 2.5 light-years across. In our neck of the galaxy that distance is just over half way from our Sun to its nearest stellar neighbors in the Alpha Centauri star system. The massive star NGC 2264 IRS, seen by Hubble's infrared camera in 1997, is the likely source of the wind sculpting the Cone Nebula and lies off the top of the image. The Cone Nebula's reddish veil is produced by glowing hydrogen gas.
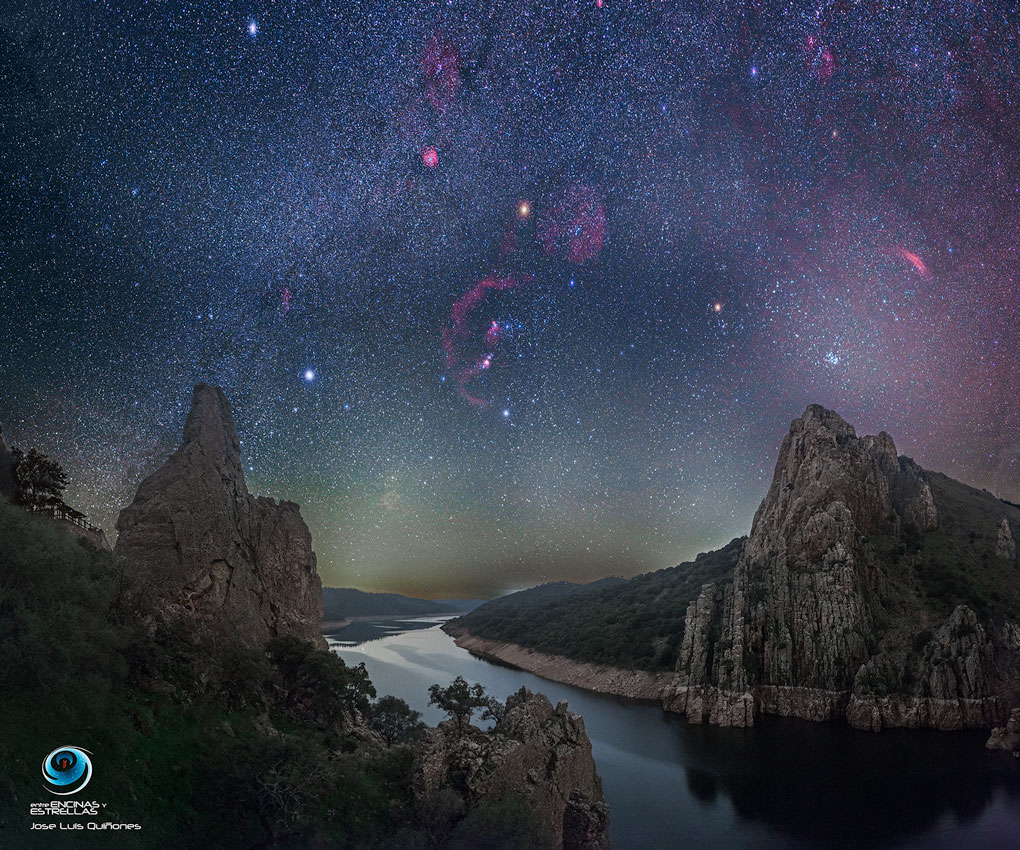 A Dark Winter Sky over Monfragüe National Park in Spain
A Dark Winter Sky over Monfragüe National Park in Spain
Image Credit & Copyright: José Luis Quiñones (Entre Encinas y Estrellas)
Explanation: You, too, can see a night sky like this. That is because Monfragüe National Park in Spain, where this composite image was created, has recently had its night sky officially protected from potential future light pollution. Icons of the night sky that should continue to stand out during northern winter -- and are visible on the featured image -- include very bright stars like Sirius, Betelgeuse, and Procyon, bright star clusters like the Pleiades, and, photographically, faint nebulas like the California and Rosette Nebulas. Even 100 years ago, many people were more familiar with a darker night sky than people today, primarily because of the modern light pollution. Other parks that have been similarly protected as dark-sky preserves include Death Valley National Park (USA) and Grasslands National Park (Canada). Areas such as the city of Flagstaff, Arizona and much of the Big Island of Hawaii also have theirnight skies protected.
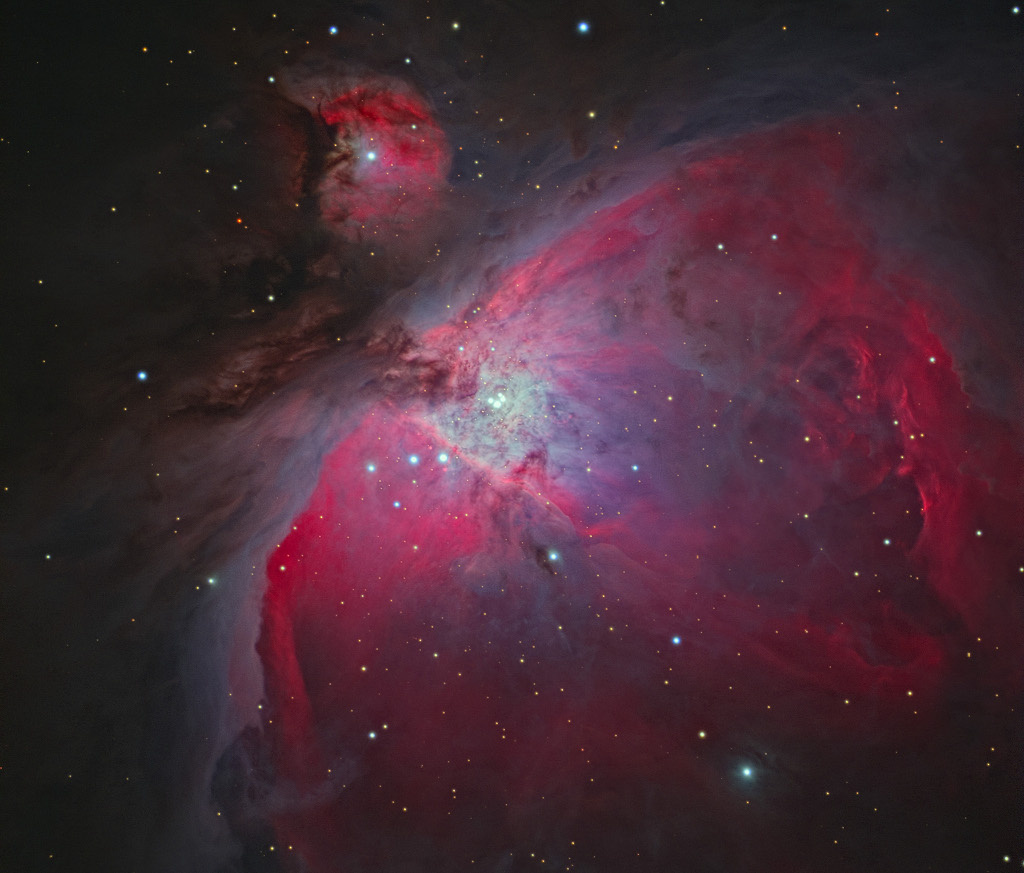 At the Heart of Orion
At the Heart of Orion
Image Credit & Copyright: Christoph Kaltseis, CEDIC 2017
Explanation: Near the center of this sharp cosmic portrait, at the heart of the Orion Nebula, are four hot, massive stars known as the Trapezium. Tightly gathered within a region about 1.5 light-years in radius, they dominate the core of the dense Orion Nebula Star Cluster. Ultraviolet ionizing radiation from the Trapezium stars, mostly from the brightest star Theta-1 Orionis C powers the complex star forming region's entire visible glow. About three million years old, the Orion Nebula Cluster was even more compact in its younger years and a dynamical study indicates that runaway stellar collisions at an earlier age may have formed a black hole with more than 100 times the mass of the Sun. The presence of a black hole within the cluster could explain the observed high velocities of the Trapezium stars. The Orion Nebula's distance of some 1,500 light-years would make it the closest known black hole to planet Earth.
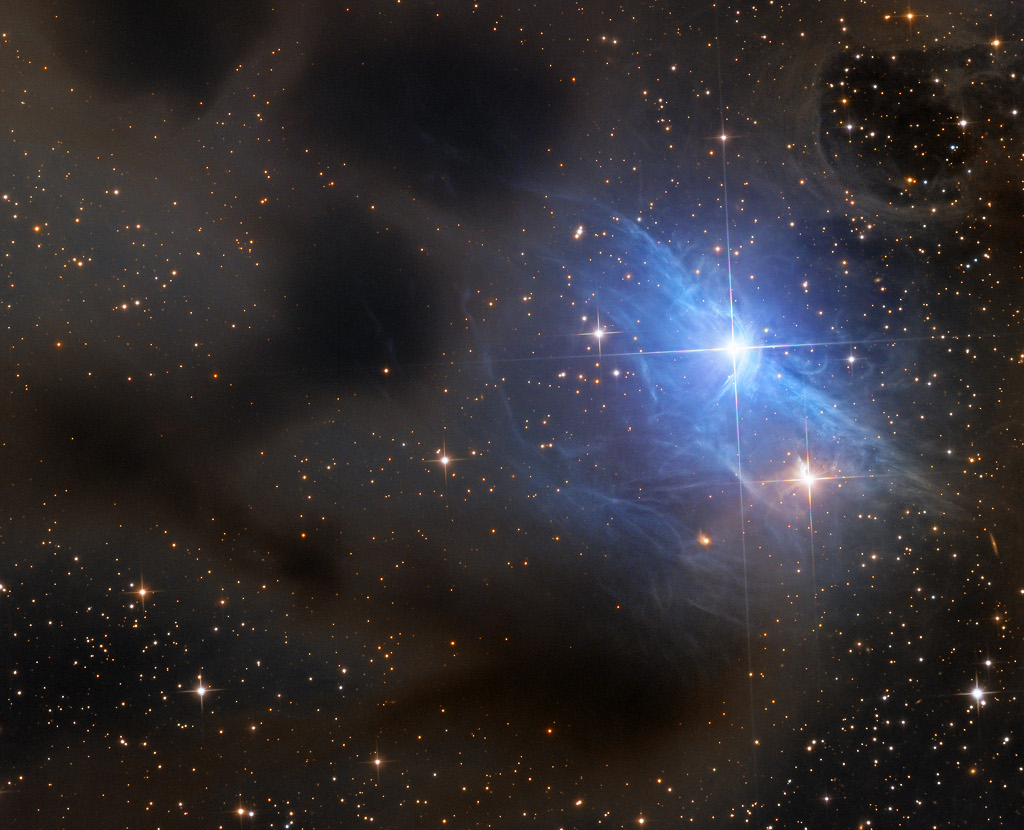 Reflections on vdB 31
Reflections on vdB 31
Image Credit & Copyright: Adam Block, Mt. Lemmon SkyCenter, U. Arizona
Explanation: Riding high in the constellation of Auriga, beautiful, blue vdB 31 is the 31st object in Sidney van den Bergh's 1966 catalog of reflection nebulae. It shares this well-composed celestial still life with dark, obscuring clouds recorded in Edward E. Barnard's 1919 catalog of dark markings in the sky. All are interstellar dust clouds, blocking the light from background stars in the case of Barnard's dark nebulae. For vdB 31, the dust preferentially reflects the bluish starlight from embedded, hot, variable star AB Aurigae. Exploring the environs of AB Aurigae with the Hubble Space Telescope has revealed the several million year young star is itself surrounded by flatteneddusty disk with evidence for the ongoing formation of a planetary system. AB Aurigae is about 470 light-years away. At that distance this cosmic canvas would span about four light-years.
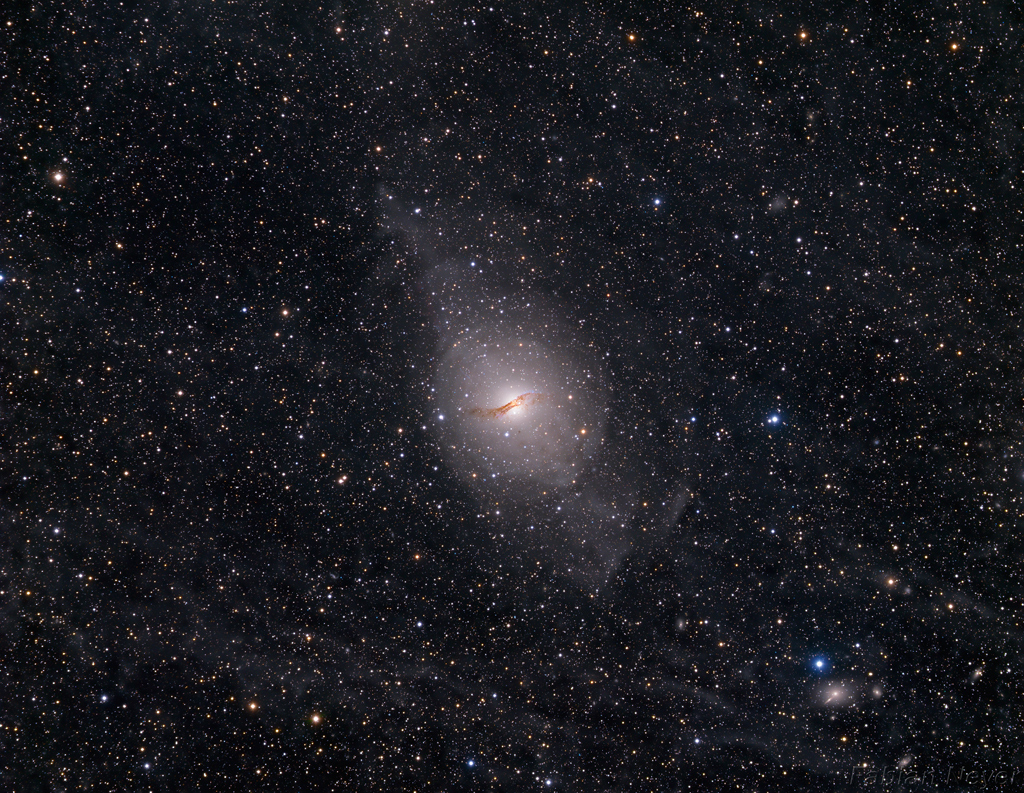 Centaurus A
Centaurus A
Image Credit & Copyright: Fabian Neyer
Explanation: Only 11 million light-years away, Centaurus A is the closest active galaxy to planet Earth. Spanning over 60,000 light-years, the peculiar elliptical galaxy also known as NGC 5128, is featured in this sharp telescopic view.Centaurus A is apparently the result of a collision of two otherwise normal galaxies resulting in a fantastic jumble of star clusters and imposing dark dust lanes. Near the galaxy's center, left over cosmic debris is steadily being consumed by a central black hole with a billion times the mass of the Sun. As in other active galaxies, that process likely generates the radio, X-ray, and gamma-ray energy radiated by Centaurus A. The remarkably deep, visible light image offers further evidence of the ensuing cosmic violence in the faint shells and extended features surrounding the active galaxy.
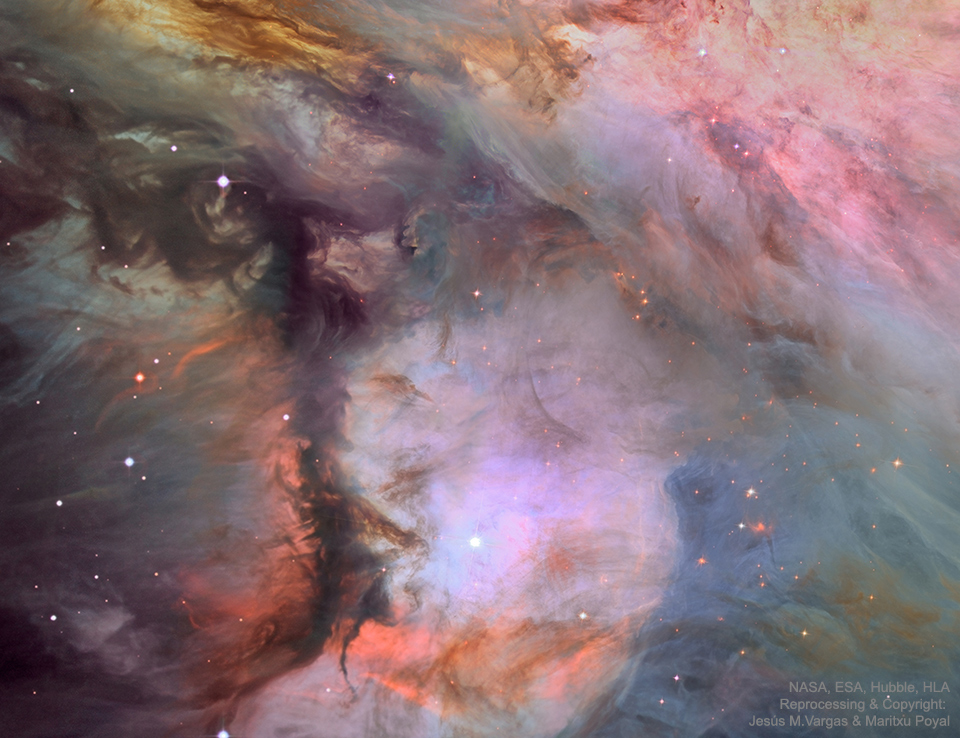 Dust, Gas, and Stars in the Orion Nebula
Dust, Gas, and Stars in the Orion Nebula
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble, HLA; Reprocessing & Copyright: Jesús M.Vargas & Maritxu Poyal
Explanation: The Great Nebula in Orion, an immense, nearby starbirth region, is probably the most famous of all astronomical nebulas. Here, filaments of dark dust and glowing gas surround hot young stars at the edge of an immenseinterstellar molecular cloud only 1500 light-years away. In the featured deep image shown in assigned colors, part of the nebula's center is shown as taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. The Great Nebula in Orion can be found with the unaided eye near the easily identifiable belt of three stars in the popular constellation Orion. In addition to housing a bright open cluster of stars known as the Trapezium, the Orion Nebula contains many stellar nurseries. These nurseries contain much hydrogen gas, hot young stars, proplyds, and stellar jets spewing material at high speeds. Also known as M42 and M43, the Orion Nebula spans about 40 light years and is located in the same spiral arm of our Galaxy as the Sun.








